Whether you are an athlete in training or simply someone who wants to improve their gym efforts then it is incredibly important to pay attention to your diet. In the following article we are going to take a look at the ways in which you can embrace this concept and build on your understanding. In doing so we hope that you will be able to reach your goals with greater ease and boost your overall health.
Understanding the different energy systems in the body can go a long way to helping you understand why different foods should be included.
Adenosine Triphosphate
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is a complex chemical that is key for many processes in the body. It must be present in order that the muscles are able to contract. When stores of ATP become depleted then it is necessary for these stores to be replenished before the muscles can continue to contract properly. Physically exerting yourself for an extended period of time will cause the depletion of ATP stores.
As the amount of ATP in the muscles decreases, the function can be preserved for a short period by the presence of creatine phosphate. Following this, there will be a shift to the glycolytic system.
The Glycolytic Energy System
This energy system is fuelled by dietary carbohydrates and is capable of providing a lot of power for the body to use. However it does not do so as efficiently or effectively as ATP does. The glycolytic system has a bigger fuel supply than the ATP system and won’t fatigue as quickly.
After approximately 10 seconds of intense exercise the glycolytic system will kick in to contribute towards energy production. After around 30 seconds of continued intense exercise, this system will usually be largely responsible for energy.
Different Types of Fuel
There are different types of fuel that contribute to each of the energy systems and we are going to now outline some of the most important ones!
Creatine Phosphate
Creatine phosphate is used to make ATP only under conditions that require 100% effort for very short periods of time. This molecule serves as a fast-acting energy supply. It is stored in the muscle cells and will be broken down quickly to create ATP when required.
Fat and Carbohydrates
The body can utilise dietary fats and carbohydrates for ATP synthesis.
Carbohydrates are stored in the liver and the muscles as glycogen. During short periods of high intensity anaerobic exercise (such as sprinting) the body will rely on carbohydrates for energy. This is because fat cannot be used for energy in the absence of oxygen, and anaerobic exercise requires oxygen. Aerobic exercise, on the other hand, will use a combination of fat and carbohydrates
When a person is undertaking exercise then fat stores from all over the body can be utilised for energy. During this time, the fat needs to be transported to the muscles through the blood.
Eating for Optimum Energy
When you are exercising it is important that your glycogen levels are at an adequate level. This is because exercising when glycogen levels are low can mean that your performance is hindered and that muscle loss occurs as this lean body tissue is broken down. Exercising with low glycogen stores can also mean that fat is used for energy less effectively.
When eating to improve sports performance it is important to include foods that are full of nutrients and antioxidants, as well as those that have anti-inflammatory properties. So, what are some of the best foods that you can add to your diet in order to enhance your sports performance?
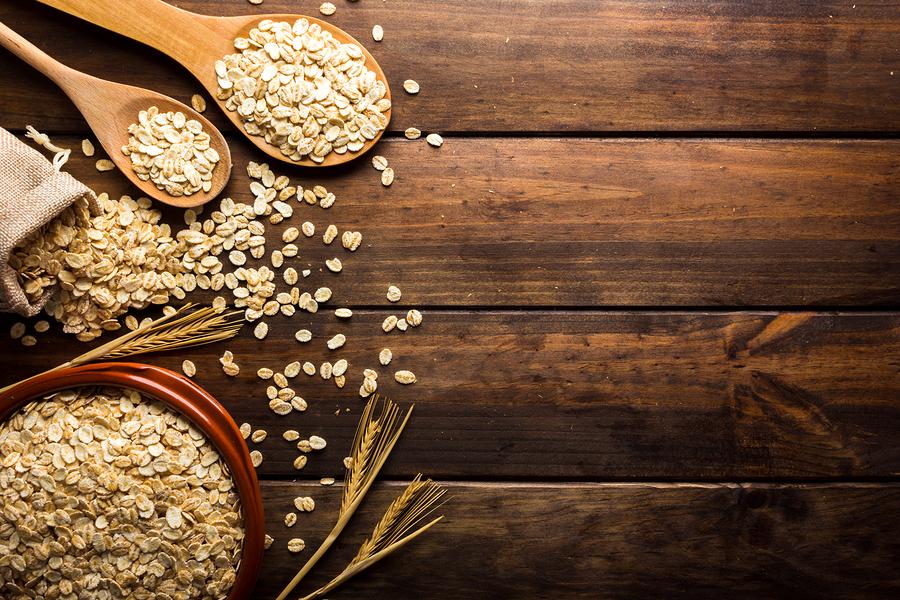
Oats
This heart healthy whole grain is a favourite breakfast choice among those who want to take care of themselves. The high fibre count of oats means that they are useful for absorbing unwanted cholesterol and fat from the bloodstream. Oats are also an abundant source of carbohydrates, which are an essential energy source.
When you eat oats for breakfast you will be setting yourself up to have more consistent energy levels during your day. Overnight oats are a delicious way to include oats in your day and you can click here to find out more about this dish!
Blueberries
Regularly labelled as a super food, blueberries serve as a tasty snack and can also be added to countless recipes.
The high antioxidant count of blueberries means that they are very beneficial to the body as they can help to reduce oxidative damage. Put simply, they can help to protect the cells of the body from harm and damage. Although exercise is undoubtedly good for us, it can cause cell damage when it is particularly strenuous. Consuming blueberries can help to protect against this damage whilst also boosting the immune system and contributing to energy levels.
Cruciferous Vegetables
Cruciferous vegetables are a rich source of polyphenols, which are natural compounds with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Aiming to eat a range of these vegetables, such as broccoli, cabbage and cauliflower will help to give you a healthy boost.
References
Related Posts
Cigarettes May Inhibit Inflammation Treatments
Axial spondyloarthritis, also known as AxSpa, is a chronic…