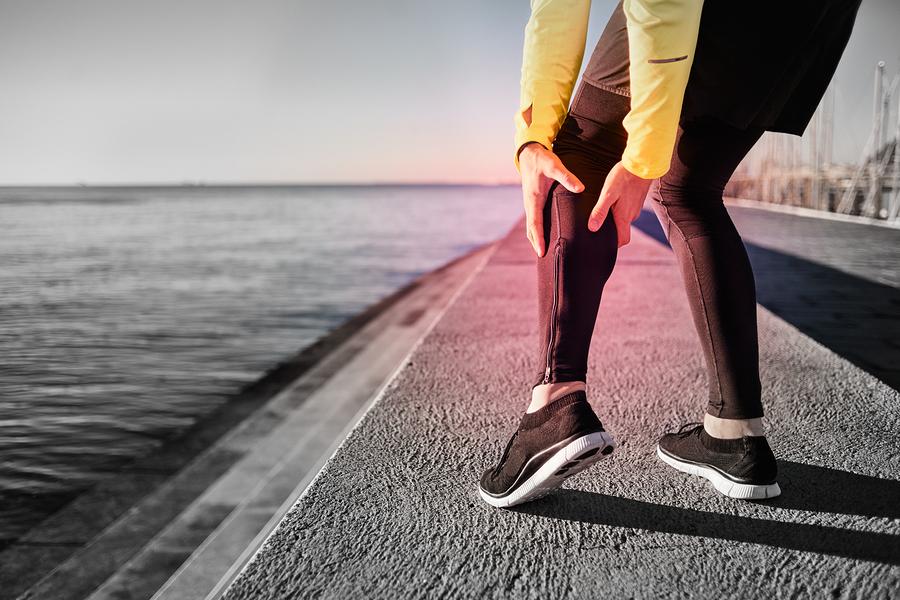
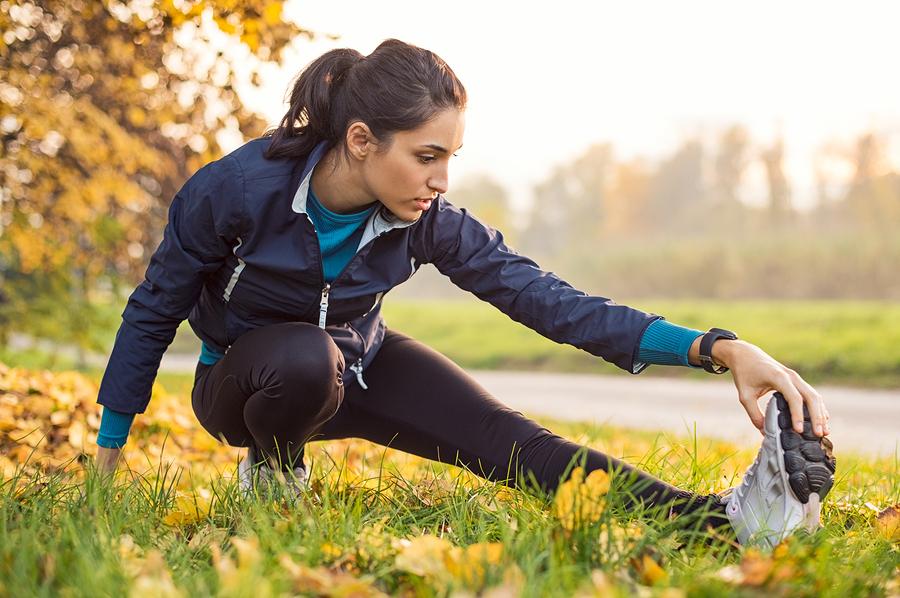
Muscle cramps occur when any of our muscles contract, either forcibly or involuntarily, and then does not relax as it should. This is often referred to as a spasm and can happen for a range of reasons. It is something that the majority of people will experience in their lives, albeit some more than others! Although a muscle cramp will usually only happen for a few seconds, it can last up to 15 minutes. It will rarely ever be longer than this.
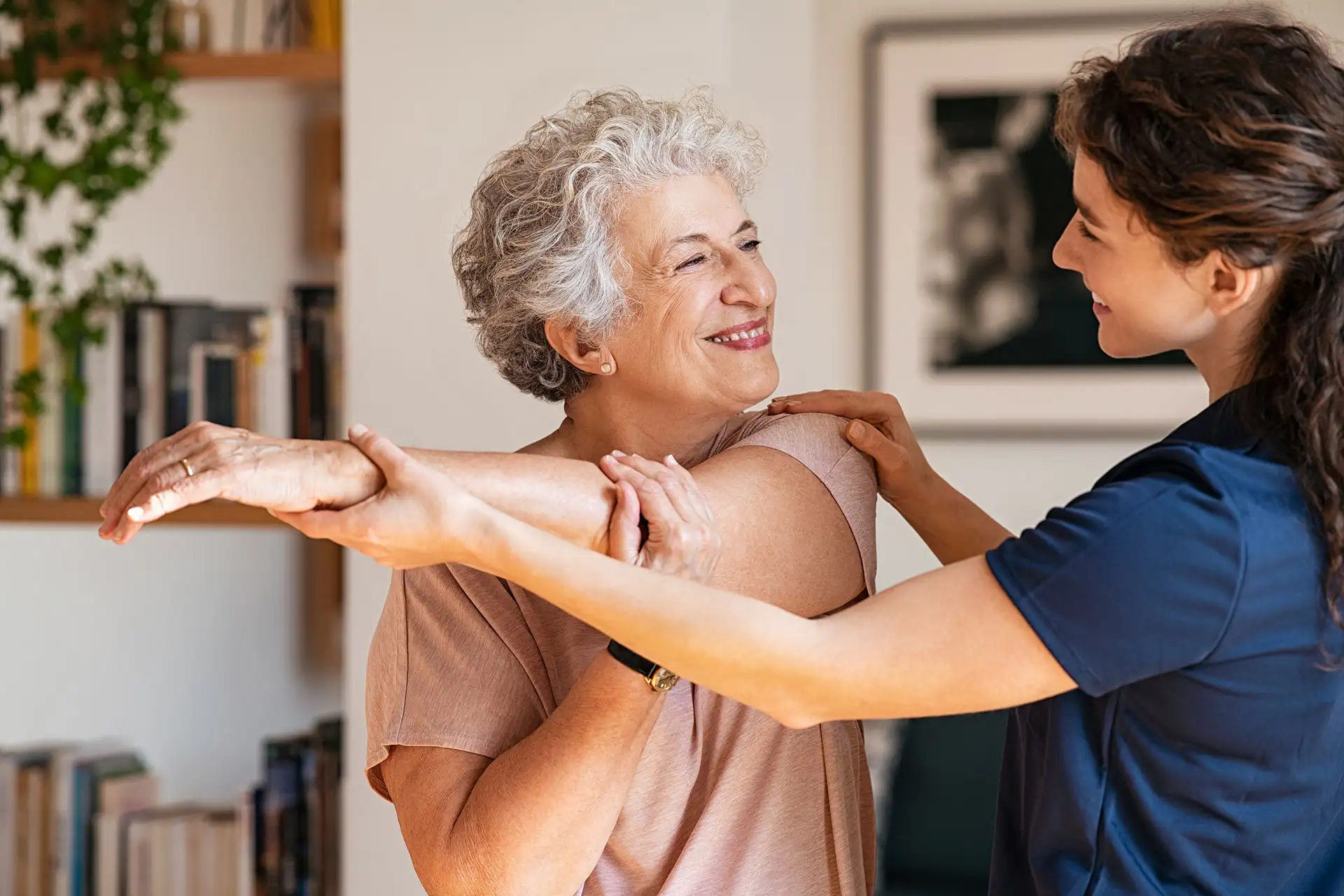
When we move, our muscles are constantly at work contracting and relaxing to support our movement. Additionally, the muscles in our neck and head are also constantly at work in order that we maintain our posture. Our muscles are one of the most important parts of the body and their health and function should always be considered a priority!
There are four main different types of muscle cramps. These four are known as true cramps, dystonic cramps, contractures and tetany. Let’s analyse these four different types of cramp and also take a quick look at what the causes for them are!
True Cramps
First of all, true cramps are when part or all of either one muscle or a group of muscles cramps. This can either be caused by injury, strenuous activity, low blood calcium, dehydration, low potassium, or simply because the muscle has been resting for a long period of time.
Experts are generally in agreement that true cramps occur because the nerves become over stimulated by any one or more of the aforementioned factors.
Dystonic Cramps
Secondly, dystonic cramps happen when your body moves in some way and muscles that are not needed for this specific action contract anyway.
Dystonic cramps are especially common when performing repetitive activities, such as typing on a keyboard or playing an instrument.
Contractures
Thirdly, contractures are continuous involuntary contractions of a muscle and also sometimes of the fibers surrounding the affected muscle.
Athletes are at particular risk of experiencing a contracture and it can occur both before and after exercise. This kind of muscle cramp is caused when metabolites accumulate and the blood supply is restricted. Excessive muscle fatigue is also a risk factor.
Tetany
Finally, tetany is the experience of the nerve cells in the body activating and stimulating the muscles. This can cause spasms throughout the body and is likely to happen when levels of calcium and magnesium are low. When these two things have only a slight presence in the body, the activity of nerve tissue is increased, leading to cramping.
Causes of Cramps
Even though muscle cramps are usually brought on by over-exertion or improper use, they can also be caused by certain types of medication. As we get older we are also much more likely to experience cramping of the muscles.
Preventing Cramps
There are several different scenarios in which you are at a heightened risk of experiencing cramps, such as if you are exercising, or putting your body through an unfamiliar activity.
If you believe yourself to be in a situation where the potential for cramping is heightened, then you can take steps to alleviate the impact and reduce your risk of suffering with this issue.
If muscles are stretched before they are used then this can greatly help to avoid any cramps happening. This is something that you should do in the majority of instances where you are going to exert yourself in some way, such as if you are going to the gym or going for a jog. It is also then of course something you should do in more extreme circumstances, such as running a marathon!
Stretching the muscles tells your body that they are about to be engaged, and helps with the process of warming them up for use.
Staying hydrated and adequately nourishing your body through your diet are also good ways to keep this painful problem at bay. There has been some research to suggest that drinking electrolytes during intense exercise can help to prevent the problem of cramps, or at least lower the risk.
It has also been suggested that under-consumption of carbohydrates before exercise could increase the risk of cramps occurring. This is largely because carbohydrates are the primary energy source of the body. When we consume carbohydrates it eventually becomes stored as glycogen inside of our muscles. During exercise, glycogen stores will be called upon, and once these stores are depleted, then cramps could present.
Finally, if you are an athlete and know that you are going to be taking part in an event, then ensuring you do an adequate amount of training will help to prepare the body for what is about to come. This will then lower the chance of cramps, or other performance hindering issues, arising.
References
1) http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/muscle-cramp/basics/definition/con-20014594
Related Posts
Cigarettes May Inhibit Inflammation Treatments
Axial spondyloarthritis, also known as AxSpa, is a chronic…